Understanding LangChain in One Article: Building Powerful Applications with Large Language Models
Understanding LangChain in One Article: Building Powerful Applications with Large Language Models
Starting with the architecture diagram, step by step, this article helps you understand all aspects of LangChain.
- What is LangChain?
- What Information Does the LangChain Architecture Diagram Tell Us?
- Essential Core Modules You Need to Know
- Experience the Function of Each Module Through Simple Example Code
1. What is LangChain?
LangChain is an open-source framework for quickly building LLM (Large Language Model) applications.
It abstracts some common behaviors used in LLMs, encapsulates them as APIs, unifies the usage methods, and simplifies the development process.
2. What Information Does the LangChain Architecture Diagram Tell Us?
The architecture diagram of LangChain is as follows:
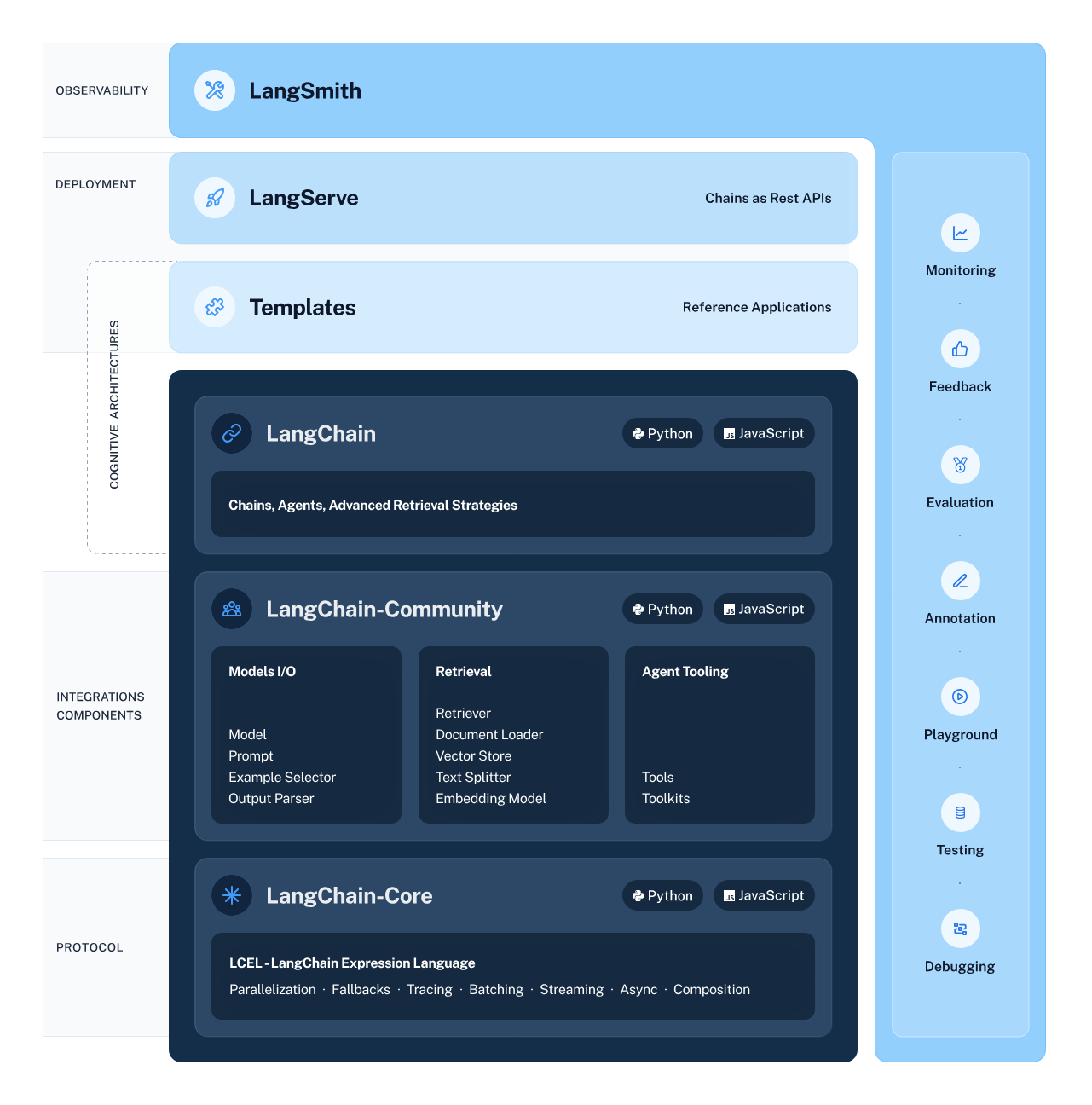
What information can we obtain from the architecture diagram?
2.1. The Ecosystem of LangChain
The ecosystem of LangChain, besides LangChain itself, also includes LangServe and LangSmith.
- LangChain focuses on development
- LangServe is used for deployment
- LangSmith serves as an observability platform
Note: For beginners, LangServe and LangSmith can be initially overlooked. This article focuses only on LangChain itself.
2.2. Development Language of LangChain Source Code
The source code of LangChain is developed in two languages: Python and JavaScript.
- The GitHub repository for the Python source code:https://github.com/langchain-ai/langchain
- The GitHub repository for the JavaScript source code:https://github.com/langchain-ai/langchainjs
Note: This article will focus on LangChain's Python source code.
2.3. Organization of LangChain's Source Code
The libs directory in the LangChain source code is the primary directory, containing three main packages: LangChain, LangChain-Community, and LangChain-Core.
- LangChain-Core package: The foundation of the framework
- LangChain-Community package: Integrated components/third-party components
- LangChain package: Core components. The contents of both LangChain-Core and LangChain-Community packages are imported into this LangChain package. LangChain package serves as the entry point, calling components from both LangChain-Core and LangChain-Community packages
3. Essential Core Modules You Need to Know
3.1. Model I/O
Usage: Abstracts interaction with LLM, divided into Prompts module, Language Model module (LLM module), and Output Parsers module.
3.1.1. Prompts
Usage: Uses Prompt templates as inputs for LLM.
3.1.2. Language Model(LLM)
Usage: An abstraction of the language model, calls LLM through a universal interface.
3.1.3. Output Parsers
Usage: Parses the output of LLM, able to parse into different formats.
3.2. Chains
Usage: Combines multiple components to create a single cohesive task. Multiple Chains can be nested or combined with other components to build more complex Chains.
3.3. Agents
Usage: Based on user input, plans and makes decisions using LLM. It can divide tasks into smaller parts or decide the behavior of each step, integrating various tools and dynamically choosing whether to use a tool and which tool to use.
Key Concepts:
- Agent: An Agent makes a decision based on the current situation. It dynamically decides whether to respond directly or use a tool, and if using a tool, which one to choose.
- AgentExecutor: Essentially a Chain, AgentExecutor is an iterator for the Agent. It repeatedly calls the Agent to make decisions until a satisfactory result is achieved or a predefined limit is reached.
AgentExecutor can be seen as an intelligent entity, and Agent is like the brain of this entity. When a user asks a question, AgentExecutor thinks once or multiple times, i.e., it calls the Agent to make decisions until it reaches a satisfactory result or the predefined limit.
3.4. Retrieval
Usage: An abstraction of integrated data sources, including data loading, processing, vectorization, storage, and retrieval, allowing users to have their knowledge base.
3.5. Callbacks
Usage: Records relevant information during the execution of a Chain, typically used for logging, recording intermediate steps, recording token usage for billing, and controlling flow rate.
3.6. Memory
Usage: Records historical conversations to supplement historical context in subsequent dialogues, enabling the model to have continuous conversations.
4. Experience the Function of Each Module Through Simple Example Code
Note: Focus on the code flow rather than the details.
4.1. Application of Model I/O and Chains Module: Combining Prompt, LLM, and Output Parser into a Chain
from langchain_core.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
from langchain_core.output_parsers import StrOutputParser
# set Prompt
prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([
("system", "You are world class technical documentation writer."),
("user", "{input}")
])
# set LLM
llm = ChatOpenAI(openai_api_key="...")
# set Output Parser
output_parser = StrOutputParser()
# combining Prompt, LLM, and Output Parser into a Chain
chain = prompt | llm | output_parser
# invoke Chain
chain.invoke({"input": "how can langsmith help with testing?"})
4.2. Application of Retrieval Module: Building a knowledge base and retrieving relevant information as part of the Prompt
- This case demonstrates the nested combination of Chains
- The Retrieval Chain receives user input, searches for relevant documents, then combines these documents with the original user input to form a Prompt, which is then passed to the large language model (LLM) to answer the original question
from langchain_community.document_loaders import WebBaseLoader
from langchain_openai import OpenAIEmbeddings
from langchain_community.vectorstores import FAISS
from langchain.text_splitter import RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter
from langchain.chains.combine_documents import create_stuff_documents_chain
from langchain.chains import create_retrieval_chain
# data loader
loader = WebBaseLoader("https://docs.smith.langchain.com/overview")
# load data
docs = loader.load()
# text splitter
text_splitter = RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter()
# split text
documents = text_splitter.split_documents(docs)
# embedding model
embeddings = OpenAIEmbeddings()
# vectorize documents and store them in a vector database
vector = FAISS.from_documents(documents, embeddings)
# use the vector database as a retriever
retriever = vector.as_retriever()
# set Prompt
prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_template("""Answer the following question based only on the provided context:
<context>
{context}
</context>
Question: {input}""")
# combine LLM with Prompt into a Chain, where llm is from the first example.
document_chain = create_stuff_documents_chain(llm, prompt)
# combine the retriever and other Chains into a searchable Chain
retrieval_chain = create_retrieval_chain(retriever, document_chain)
# invoke retrieval_chain
response = retrieval_chain.invoke({"input": "how can langsmith help with testing?"})
# output result
print(response["answer"])
4.3. Application of Agents Module: Using the ability to retrieve from a knowledge base, search capabilities, and other skills as tools for AgentExecutor, which decomposes the user's question into multiple steps, with the Agent deciding what to do at each step
- A retriever can be used as a tool
from langchain.tools.retriever import create_retriever_tool
from langchain_community.tools.tavily_search import TavilySearchResults
from langchain.agents import create_openai_functions_agent
from langchain.agents import AgentExecutor
from langchain import hub
# retrieval tool (retrieve from the vector database), where retriever is from the second example
retriever_tool = create_retriever_tool(
retriever,
"langsmith_search",
"Search for information about LangSmith. For any questions about LangSmith, you must use this tool!"
)
# search tool (browser search for real-time information)
search_tool = TavilySearchResults(tavily_api_key="...")
# list of tools
tools = [retriever_tool, search_tool]
# obtain predefined prompts from the LangChain hub
prompt = hub.pull("hwchase17/openai-functions-agent")
# set Agent, where llm is from the first example, and tools are used to inform the Agent about the available tools and their respective functions
agent = create_openai_functions_agent(llm, tools, prompt)
# set AgentExecutor, to decompose tasks into multiple steps, with each step decided by the agent on what to do
agent_executor = AgentExecutor(agent=agent, tools=tools, verbose=True)
# query langsmith
agent_executor.invoke({"input": "how can langsmith help with testing?"})
# query weather
agent_executor.invoke({"input": "what is the weather in SF?"})
