Popular Third-party Python Packages
About 5 min
Popular Third-party Python Packages
- Numpy
- Pandas
- Requests
- Flask
- More
1. Numpy
numpy, called numeric python. It is one of the most popular packages in machine learning and data science community. It contains among other things:a powerful N-dimensional array objectsophisticated (broadcasting) functionstools for integrating C/C++ and Fortran codeuseful linear algebra, Fourier transform, and random number capabilities
1.1. Install
pip install numpy
1.2. Import&Version&Help
# 导入
import numpy
# 查看版本
print('numpy:', np.__version__)
# 查看可用方法
print(dir(np))
1.3. Create
""" array """
# np.array
np.array(sequence) # 不设定类型
np.array(sequence,dtype) # 设定类型
Note:
sequence可以是list,可以是tuple
dtype取值类型:int,float,bool,str
创建后类型为n维数组:numpy.ndarray
# 值全为0的array
# np.zeros(shape,dtype)
numpy_zeros = np.zeros((3,3),dtype=int)
# 值全为1的array
# np.ones(shape,dtype)
numpy_ones = np.ones((3,3),dtype=int)
# 值全为n的array
numpy_ns = numpy_ones * n
# numpy.arange(start, stop, step) 类似python的内置函数range
odd_numbers = np.arange(1, 20, 2)
""" matrix """
four_by_four_matrix = np.matrix(np.ones((4,4), dtype=float))
示例
# exp1
python_list = [1,2,3,4,5]
numpy_array_from_list = np.array(python_list, dtype=float)
print(type (numpy_array_from_list)) # <class 'numpy.ndarray'>
print(numpy_array_from_list) # [1., 2., 3., 4., 5.]
# exp2
python_tuple = (1,2,3,4,5)
numpy_array_from_tuple = np.array(python_tuple)
print(type (numpy_array_from_tuple)) # <class 'numpy.ndarray'>
print('numpy_array_from_tuple: ', numpy_array_from_tuple) # numpy_array_from_tuple: [1 2 3 4 5]
# exp3
four_by_four_matrix = np.matrix(np.ones((4,4), dtype=float))
print(type(four_by_four_matrix))
print(four_by_four_matrix)
1.4. Convert
# array转list
np_to_list=numpy_array.tolist()
1.5. Dtype
# 数据类型:str, int, float, complex, bool, list, None
# numpy_array所有元素都是同一类型
# 查看数据类型
numpy_array.dtype
# 转换数据类型
str_array = numpy_array.astype('str')
str_array = numpy_array.astype('float').astype('str')
示例
int_lists = [-3, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2,3]
int_array = np.array(int_lists)
print(int_array.dtype) # int64
1.6. Shape&Reshape
# numpy_array的形状:每个维度的大小
numpy_array.shape
# 改变形状:reshape & flatten
first_shape = np.array([(1,2,3), (4,5,6)])
reshaped = first_shape.reshape(3,2)
flattened = reshaped.flatten()
示例
nums = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5])
print('shape of nums: ', nums.shape) # shape of nums: (5,)
three_by_four_array = np.array([[0, 1, 2, 3],
[4,5,6,7],
[8,9,10, 11]])
print(three_by_four_array.shape) # (3, 4)
1.7. Size
# 所有元素之和
numpy_array.size
示例
numpy_array_from_list = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5])
two_dimensional_list = np.array([[0, 1, 2],[3, 4, 5],[6, 7, 8]])
print('The size:', numpy_array_from_list.size) # The size: 5
print('The size:', two_dimensional_list.size) # The size: 9
1.8. Math Operation
1、numpy_array与数字:
无需循环,会对每个元素生效
2、numpy_array与numpy_array:
相同位置进行运算
示例
numpy_array = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5])
a = numpy_array_from_list + 10
print(a) # [11 12 13 14 15]
b = numpy_array_from_list - 10
print(b) # [-9 -8 -7 -6 -5]
c = numpy_array_from_list * 10
print(c) # [10 20 30 40 50]
d = numpy_array_from_list / 10
print(d) # [0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5]
e = numpy_array_from_list % 3
print(e) # [1 2 0 1 2]
f = numpy_array_from_list // 10
print(f) # [0 0 0 0 0]
g = numpy_array_from_list ** 2
print(g) # [ 1 4 9 16 25]
np_list_one = np.array([1,2,3])
np_list_two = np.array([4,5,6])
print(np_list_one + np_list_two) # [5 7 9]
print(np_list_one * np_list_two) # [4 10 18]
1.9. 切片 Slice
# 行
numpy_array[0] # 第1行
numpy_array[1] # 第2行
numpy_array[2] # 第3行
# 列
numpy_array[:,0] # 第1列
numpy_array[:,1] # 第2列
numpy_array[:,2] # 第3列
# 元素
numpy_array[1,1] = 55
# 前2行,前2列
numpy_array[0:2,0:2]
# 翻转
numpy_array[::-1,::-1]
示例
numpy_array = np.array([[1,2,3],[4,5,6], [7,8,9]])
numpy_array[::-1,::-1]
""" result:
array([[9, 8, 7],
[6, 5, 4],
[3, 2, 1]])
"""
1.10. 连接 hstack&vstack
1、水平连接(按行)h=Horizontal:np.hstack((np_list_one,np_list_two))
2、垂直连接(按列)v=Vertical :
np.vstack((np_list_one,np_list_two))
a = np.array((1,2,3))
b = np.array((4,5,6))
print(np.hstack((a,b)))
"""
[1 2 3 4 5 6]
"""
print(np.vstack((a,b)))
"""
[[1 2 3]
[4 5 6]]
"""
a = np.array([[1],[2],[3]])
b = np.array([[4],[5],[6]])
print(np.hstack((a,b)))
"""
array([[1, 4],
[2, 5],
[3, 6]])
"""
1.11. Statistic
- Numpy Functions
- Min np.min()
- Max np.max()
- Mean np.mean()
- Varience
- Percentile
- Standard deviation np.std()
1.12. Random
1、float
random_float = np.random.random()
2、float array
random_floats = np.random.random(5)
3、int(start,end)左闭右开
random_int = np.random.randint(0, 11)
4、int array (start,end,size)左闭右开
random_int = np.random.randint(2,10, size=4)
random_int = np.random.randint(2,10, size=(3,3))
5、normal array (均值mu,标准差sigma,size)
normal_array = np.random.normal(79, 15, 80)
示例
normal_array = np.random.normal(79, 15, 80)
print(normal_array)
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns
sns.set()
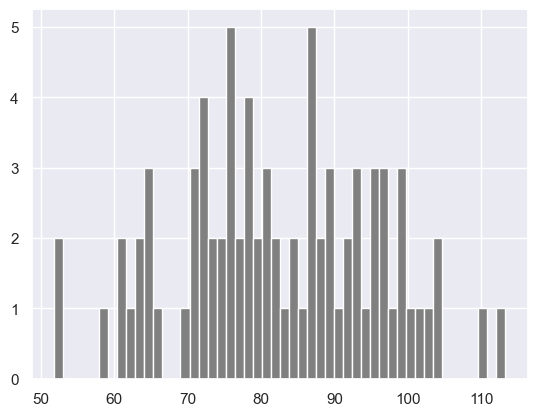
plt.hist(normal_array, color="grey", bins=50)
"""normal_array 结果
80个元素的数组,服从均值为79,标准差为15的正态分布
"""
array([ 92.69419484, 100.90522098, 75.66676723, 51.85288324,
58.93456584, 86.8882653 , 77.85232879, 80.65229762,
75.29982406, 61.37092068, 92.2196512 , 81.4621436 ,
75.60624329, 78.8313502 , 95.1988703 , 71.61367817,
76.53464648, 79.79467471, 84.64456654, 60.45380126,
86.26484877, 89.34976733, 76.31257666, 73.19016742,
87.32942795, 89.14391161, 104.4921231 , 93.81488786,
75.73943026, 65.22710178, 92.4933286 , 91.04748818,
88.43185823, 71.7591173 , 76.58885905, 70.56334243,
96.84237334, 80.68069405, 78.58849189, 74.96428085,
70.93466647, 65.15164539, 73.95878663, 99.15939347,
63.39133723, 78.79097971, 85.53327827, 101.79255722,
63.52833828, 86.50269085, 104.36624717, 89.25578975,
79.45701012, 81.03987345, 72.25460386, 95.33397222,
95.60863274, 82.27517837, 83.72772366, 71.53024163,
109.75087739, 97.12307579, 92.74977091, 69.97209205,
96.37927411, 91.41644221, 72.94486545, 113.25565357,
99.60227425, 98.44423374, 98.68006829, 62.1570979 ,
102.71289562, 87.29671601, 71.36173083, 88.64526558,
52.90835334, 84.34055885, 64.30992424, 65.63687458])
"""plt.hist结果
array 的第一个元素:50个元素,是每个分桶的高度
array 的第二个元素:51个元素,是区间范围。此处是等宽分组。
从头到尾,每个区间范围的宽度是非常固定的约为0.76。
在默认情况下,plt.hist() 函数使用的是等宽分组
区间间隔一致的是等宽分组
区间间隔不一致,使每个区间内数据数量大致相同的是等频分组。
第一组(51.85 ~ 53.08 )有2个值落在这个范围内。
第二组(53.08 ~ 54.31 )有0个值落在这个范围内。
第三组(54.31 ~ 55.54 )有0个值落在这个范围内。
依此类推。
"""
(array([2., 0., 0., 0., 0., 1., 0., 2., 1., 2., 3., 1., 0., 0., 1., 3., 4.,
2., 2., 5., 2., 4., 2., 3., 2., 1., 2., 1., 5., 2., 3., 1., 2., 3.,
1., 3., 3., 1., 3., 1., 1., 1., 2., 0., 0., 0., 0., 1., 0., 1.]),
array([ 51.85288324, 53.08093864, 54.30899405, 55.53704946,
56.76510486, 57.99316027, 59.22121568, 60.44927108,
61.67732649, 62.9053819 , 64.1334373 , 65.36149271,
66.58954812, 67.81760352, 69.04565893, 70.27371434,
71.50176974, 72.72982515, 73.95788056, 75.18593596,
76.41399137, 77.64204678, 78.87010219, 80.09815759,
81.326213 , 82.55426841, 83.78232381, 85.01037922,
86.23843463, 87.46649003, 88.69454544, 89.92260085,
91.15065625, 92.37871166, 93.60676707, 94.83482247,
96.06287788, 97.29093329, 98.51898869, 99.7470441 ,
100.97509951, 102.20315491, 103.43121032, 104.65926573,
105.88732113, 107.11537654, 108.34343195, 109.57148735,
110.79954276, 112.02759817, 113.25565357]),
<BarContainer object of 50 artists>)
2. Pandas
pandas, an open source, BSD-licensed library providing high-performance, easy-to-use data structures and data analysis tools for the Python programming language.
3. Requests
Requests(HTTP 请求)
requests: is a package which we can use to send requests to a server(GET, POST, DELETE, PUT) We will see get, status_code, headers, text and json methods in requests module:
- get(): to open a network and fetch data from url - it returns a response object
- status_code: After we fetched data, we can check the status of the operation (success, error, etc)
- headers: To check the header types
- text: to extract the text from the fetched response object For txt, html, xml and other file formats we can use text.
- json: to extract json data Let's read a txt file from this website
# example 1
import requests # importing the request module
url = 'https://www.w3.org/TR/PNG/iso_8859-1.txt' # text from a website
response = requests.get(url) # opening a network and fetching a data
print(response)
print(response.status_code) # status code, success:200
print(response.headers) # headers information
print(response.text) # gives all the text from the page
# example 2
import requests
url = 'https://restcountries.eu/rest/v2/all' # countries api
response = requests.get(url) # opening a network and fetching a data
print(response) # response object
print(response.status_code) # status code, success:200
countries = response.json()
print(countries[:1]) # we sliced only the first country, remove the slicing to see all countries
4. Flask
web框架的一种前提:设置虚拟环境
5. More


